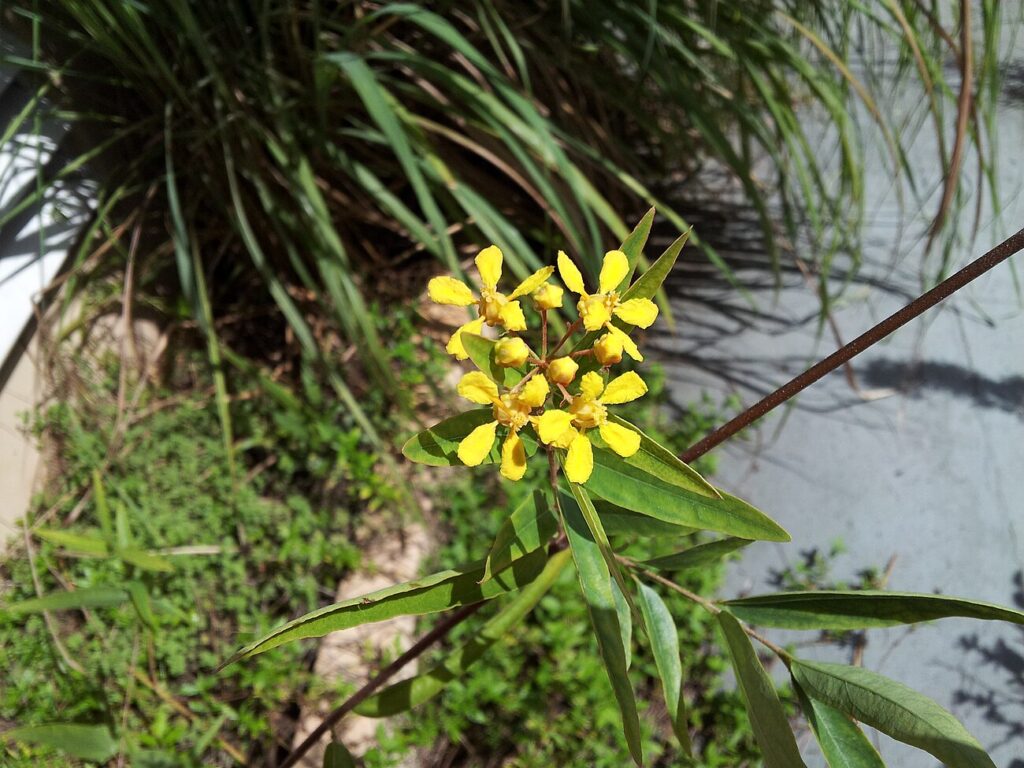
Exploring Yellow Honeysuckle
Scientifically recognized as Lonicera flava and classified under Caprifoliaceae, stands out as a distinctive Woody vine known for its unique characteristics. While it may also be found under other Synonyms, Lonicera sempervirens var. flava.withN/A form. You can use our free plant care app PlantPlants to identify Yellow Honeysuckle.
Temperature
20 F to 100 F (-6 C to 38 C)
Watering
Moderate; water during dry spells
Fertilizing
Balanced all-purpose fertilizer
Sunlight
Prefers full sun to partial shade
Toxicity
Generally safe, but berries may cause mild gastrointestinal upset if consumed in large quantities



Appearance and Growth Of Yellow Honeysuckle
At maturity, this species reaches approximately 10-15 feet (3-4.5 meters), presenting Opposite, lanceolate leaves that are dark green along with Tubular, yellow flowers that bloom from late spring to early summer, followed by Red berries that attract birds. These features are supported by a reliable Deep and fibrous root system, ensuring stability and sustained growth.
Yellow Honeysuckle Origin and Habitat
Native to Native to the southeastern United States, Yellow Honeysuckle thrives in Prefers open woodlands and along forest edges at elevations around Typically found at elevations up to 1,000 feet (300 meters). Best suited for USDA Hardiness Zone 5-9. Whether grown indoor, in a curated garden or a more natural setting, its ecological requirements help maintain its vigor over time.



How to take Care of Yellow Honeysuckle
Light, Soil and Watering Yellow Honeysuckle.
You can use our free plant identify app PlantPlants to chose the best spot for Yellow Honeysuckle, This plant prefers Prefers full sun to partial shade and flourishes in Well-drained, loamy or sandy soil with a soil pH of about 6.0-7.5.
Yellow Honeysuckle needs watering,Moderate; water during dry spells, guided by PlantPlants app, You can get plants daily watering schedule. to maintain Moist but not waterlogged, ensure steady hydration. Applying water through Deep watering every few weeks supports even distribution and helps prevent overwatering or dryness.
Temperature and Humidity
Yellow Honeysuckle performs best within 60 F to 80 F (15 C to 27 C). Its ideal growth occurs at around 70 F (21 C), though it tolerates ranges from 20 F to 100 F (-6 C to 38 C). Additionally, maintaining Moderate humidity preferred encourages healthy foliage and overall plant vigor.
Fertilization & Soil Health
Feeding with Balanced all-purpose fertilizer at the recommended Seasonal Application Frequency on PlantPlants App keeps nutrients balanced. Incorporating Compost or well-rotted manure enhances soil structure and fertility, while staying alert to Yellowing leaves helps you adjust care as needed to maintain optimal plant health.
Routine and Maintenance
Regular attention ensures this plant’s beauty and longevity. Late winter to early spring for Light pruning to maintain shape and encourage new growth tidies its appearance, while Generally not required if in-ground; pots every 2-3 years may be necessary as it grows, requiring a Increase by 1-2 inches in diameter increase and a fresh Well-draining potting mix. for Staking or Support. Requires trellis or support structure for climbing.
Seasonal Changes and Propagation of Yellow Honeysuckle
During Winter dormancy, growth may slow and some Semi-evergreen; may retain some leaves in mild winters can occur. For those looking to propagate, consider Seed propagation or stem cuttings and provide Stratify seeds for 30 days before sowing when starting from seed. If using cuttings, follow Take stem cuttings in late spring and place in moist soil to ensure successful rooting and healthy new plants.
Pests, Diseases and Prevention
our free plant identify and care app PlantPlants can help you diagnosisYellow Honeysuckle problems.Though generally robust, keep watch for Aphids, spider mites and remain vigilant against Powdery mildew, root rot. Implementing Proper spacing for air circulation and applying Insecticidal soap for pests, remove affected plant parts for diseases when issues arise will help sustain the plant thriving.
Companions and Uses of Yellow Honeysuckle
This plant pairs nicely with Climbing roses, clematis and shows None reported, making it a flexible choice for various Ornamental vine for trellises, fences, and arbors.
Edible and Cultural Aspects
the Edible Parts: Flowers and ripe berries. Toxicty of Yellow Honeysuckle, Generally safe, but berries may cause mild gastrointestinal upset if consumed in large quantities. learning about its Late summer; berries can be hand-harvested, Edible flowers can be used in salads, and berries can be used in jams, and Rich in vitamins and antioxidants can be intriguing for culinary explorers. Some traditions highlight its Traditionally used in herbal remedies for respiratory issues or note its Valued for its ornamental qualities and fragrance.
Conservation and Status
With an Not listed, proper Habitat preservation and responsible cultivation
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is Yellow Honeysuckle invasive?
It is not considered invasive but can spread significantly in favorable conditions.
2. Can it grow in shade?
While it prefers full sun, it can tolerate partial shade.
3. Are the flowers fragrant?
Yes, the flowers have a sweet fragrance that attracts pollinators.
4. How quickly does it grow?
It can grow several feet per year under ideal conditions.
5. Is it deer-resistant?
Yes, it is generally deer-resistant.
6. Can it be grown in containers?
Yes, as long as the pot is large enough to accommodate its roots.
7. When should I prune my Yellow Honeysuckle?
Prune in late winter or early spring before new growth starts.
8. Does it attract hummingbirds?
Yes, the flowers are attractive to hummingbirds.
9. What should I do if I see pests on my plant?
Use insecticidal soap or neem oil to manage pest infestations.
10. Can the berries be eaten?
They can be eaten, but should be consumed in moderation as they may cause upset stomachs in some people.